The Future of Smart Wearables: A New Era of Connected Technology
The Future of Smart Wearables: A New Era of Connected Technology
Introduction
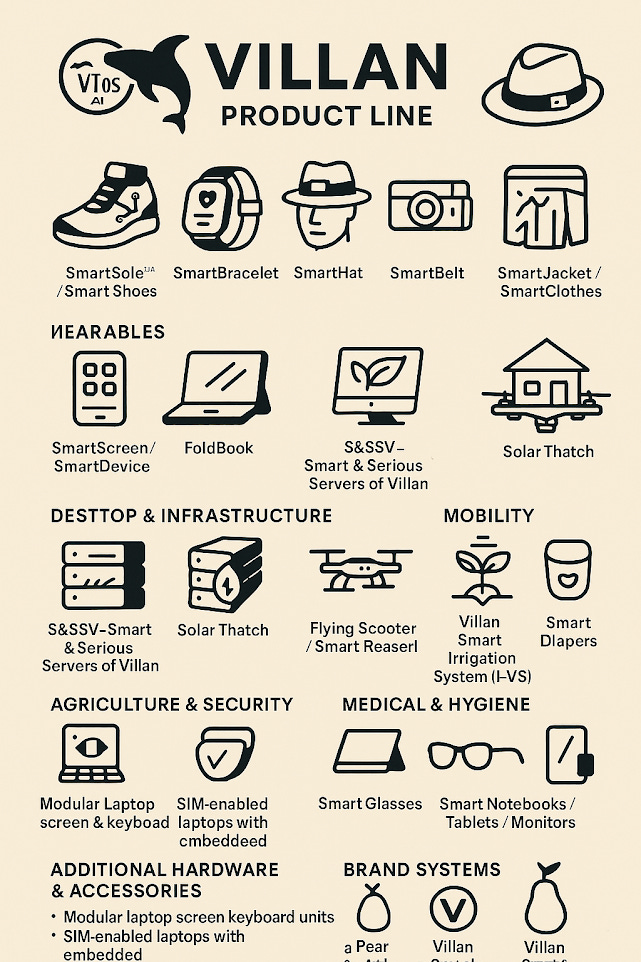
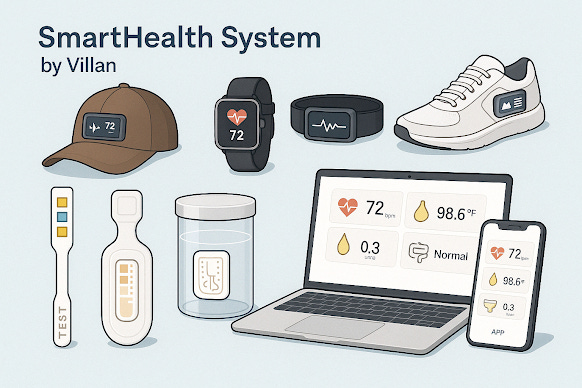
Wearable technology is undergoing a transformation, evolving from standalone gadgets into a fully integrated ecosystem that enhances human capabilities. The wearables you've envisioned—ranging from AR smart glasses to smart hats, shoes, belts, shoulders, and more—represent a groundbreaking step toward a future where digital intelligence seamlessly integrates with daily life. These devices are designed to work together, powered by a unified computing system that ensures a connected, intelligent experience.
1. The Vision for Smart Wearables
The next generation of wearables is more than just accessories—they are an extension of the human body and mind. These smart devices use artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), biometric sensors, and real-time data processing to enhance productivity, health, and everyday convenience. Key components include:
Real-time Connectivity: Wearables communicate with each other and a central operating system, ensuring seamless data exchange.
Adaptive AI Assistance: Machine learning algorithms personalize the user experience based on habits and preferences.
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: AR overlays enhance perception and interaction with the world.
Health & Performance Tracking: Advanced sensors monitor body movements, posture, and biometric data for optimal performance and safety.
2. Key Smart Wearables and Their Functions
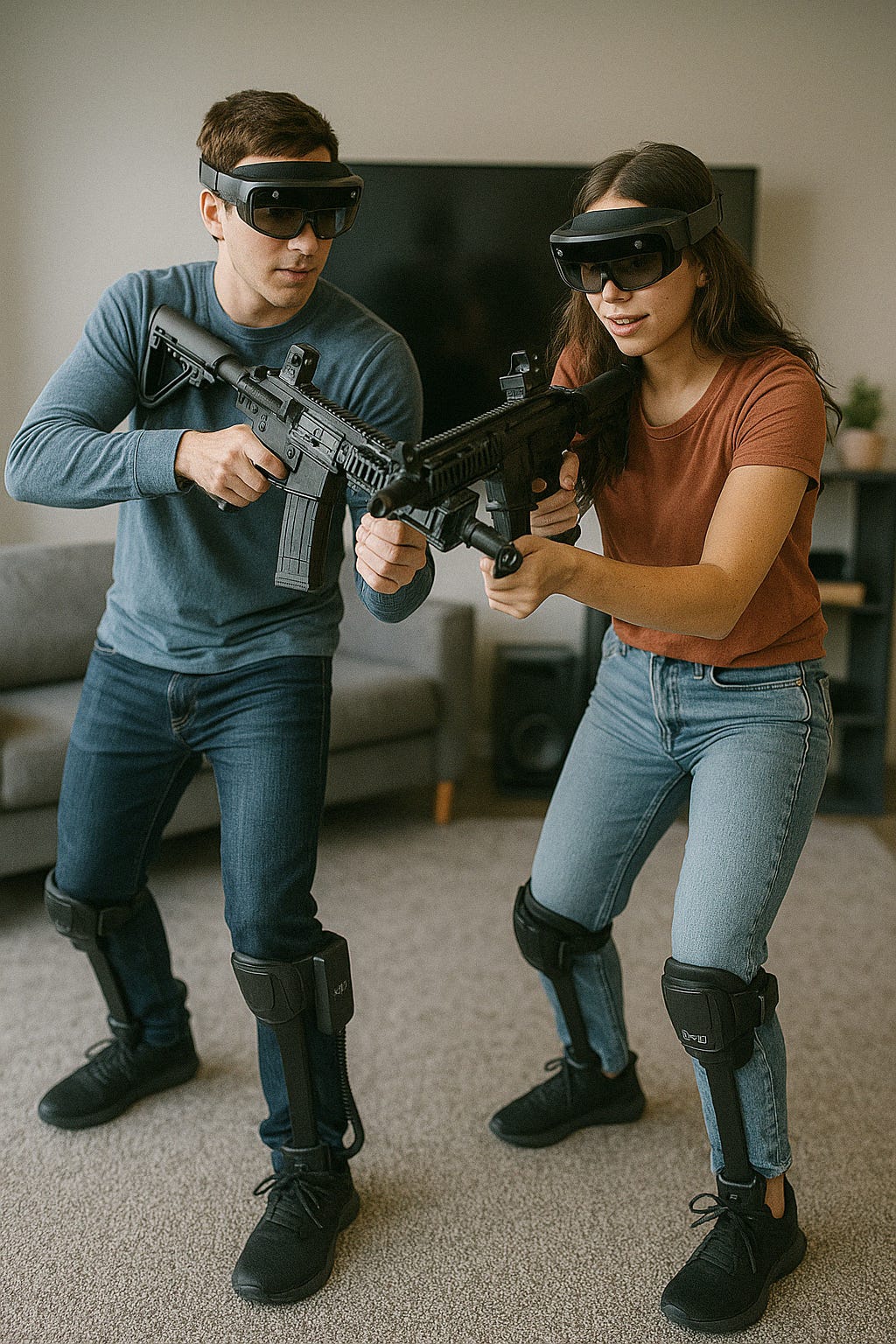
AR Smart Glasses: The Gateway to Digital Interaction
Project real-time information onto the user’s field of vision.
Provide hands-free navigation, workplace assistance, and entertainment.
Feature voice, gesture, and eye-tracking controls for seamless interaction.
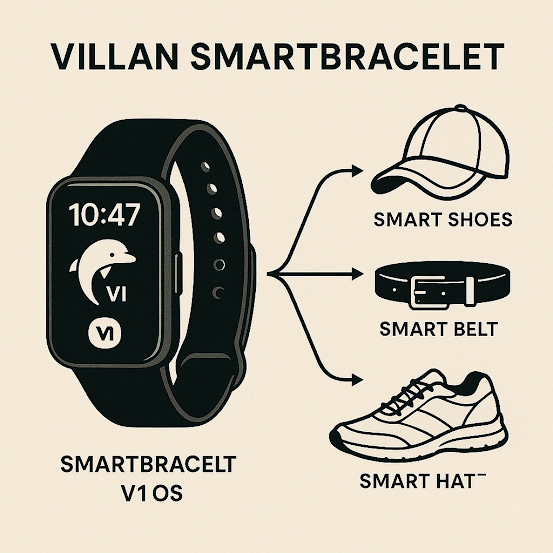
Smart Hats & Helmets: Intelligent Headgear for Safety and Communication
Offer heads-up displays (HUD) with navigation and notifications.
Include brainwave sensors for fatigue detection and cognitive monitoring.
Enable voice-controlled communication and impact detection for safety.
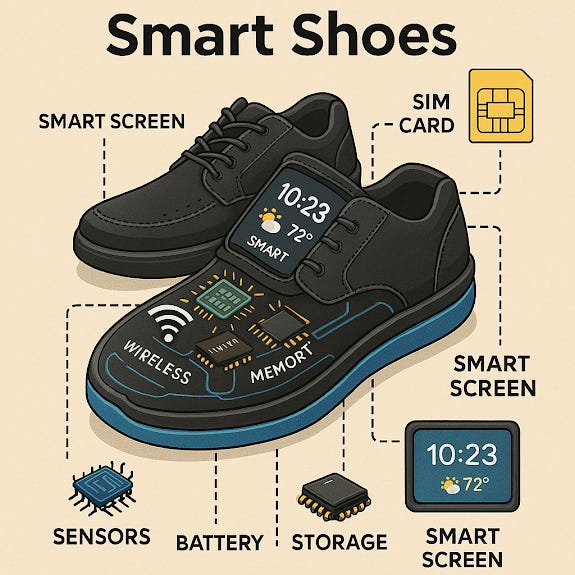
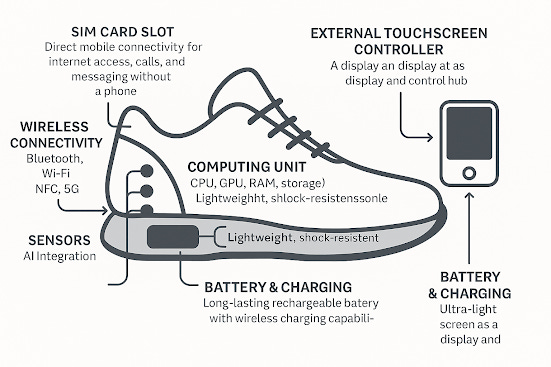
Smart Shoes: AI-Powered Mobility and Performance Enhancement
Analyze gait, posture, and movement efficiency.
Provide haptic feedback for navigation and fitness tracking.
Feature self-lacing mechanisms for automatic adjustment and support.
Smart Belts & Braces: Core Body Wearables for Health & Posture
Monitor posture and offer real-time corrective feedback.
Track biometric data such as heart rate and hydration levels.
Detect falls and send emergency alerts when needed.
Smart Shoulders: Enhancing Upper Body Functionality
Provide ergonomic support and posture correction.
Use AI to monitor muscle fatigue and prevent injuries.
Integrate with other wearables for a holistic health analysis.
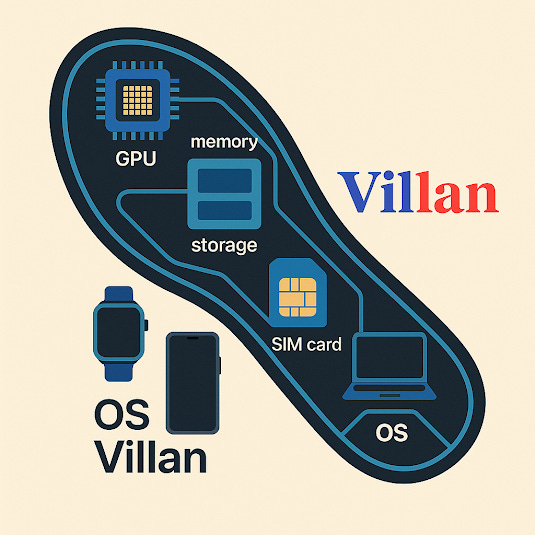
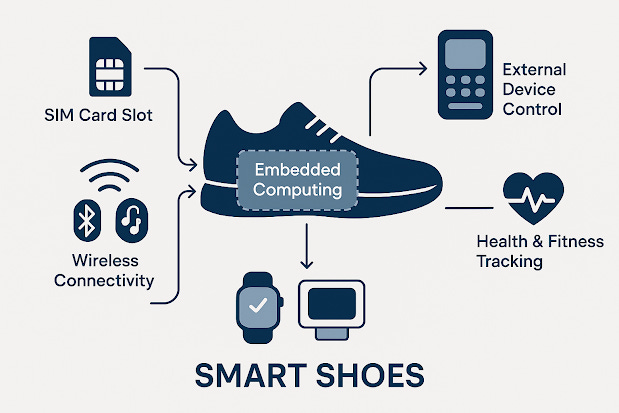
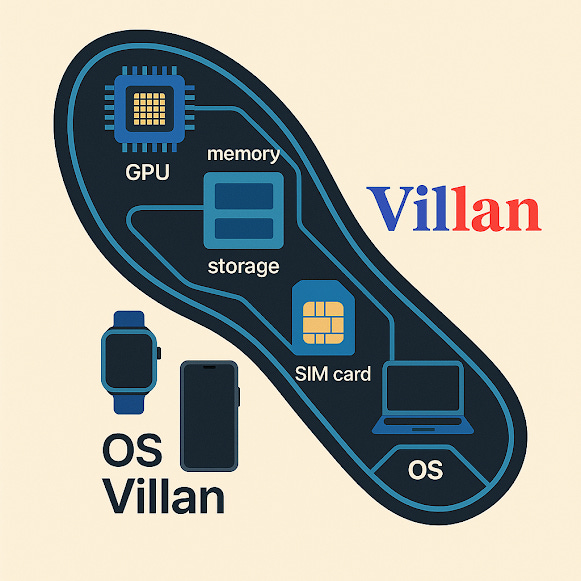
3. The Unified Computing System: Connecting All Wearables
The key to unlocking the full potential of smart wearables is a centralized computing unit that runs on a main operating system (OS). This system enables:
Cross-Device Synchronization: Wearables communicate in real-time for an interconnected user experience.
AI-Powered Insights: A single AI-driven core processes data from multiple wearables for intelligent automation.
Cloud & Edge Computing: Devices can store data locally for immediate processing or utilize the cloud for advanced analytics.
Personalized User Experience: Adaptive machine learning tailors responses and suggestions based on user behavior.
4. The Future Impact of Smart Wearables
Smart wearables are set to revolutionize industries, from healthcare and fitness to professional work and entertainment. Their ability to provide real-time data, enhance human capabilities, and create immersive digital interactions makes them essential for the future of technology. As these devices evolve, they will become indispensable tools that augment human intelligence, efficiency, and well-being.
Conclusion
The smart wearables you have envisioned are at the forefront of the next technological revolution. By integrating AI, AR, and IoT, these devices will redefine how people interact with the world, enhancing safety, performance, and daily life. The future of wearable technology is one of seamless connectivity, intelligent assistance, and boundless potential.
The Evolution of Smart Wearables: Integrating AR Smart Glasses, Smart Hats, Smart Shoes, and More
Introduction
Wearable technology has advanced beyond simple fitness trackers, evolving into a fully interconnected ecosystem of smart devices that enhance daily life, workplace efficiency, and even sports performance. Among these innovations, AR smart glasses, smart hats, smart shoes, smart belts, smart shoulders, and other wearables work together to create an integrated digital experience. These wearables incorporate sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and wireless communication to transform how users interact with their environment.
1. AR Smart Glasses: Enhancing Digital Interaction
AR smart glasses are one of the most advanced wearable technologies, overlaying digital information onto the user’s real-world view.
Core Components of AR Smart Glasses:
Waveguide Displays & MicroOLED Screens: Display digital overlays seamlessly within the user’s line of sight.
Cameras & Sensors: Capture real-world data for real-time processing, enabling object recognition and spatial mapping.
Processing Power: Onboard processors or cloud-based AI assist in rendering digital objects.
Connectivity: Equipped with Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and 5G to sync with smartphones and cloud services.
Interaction Methods: Voice control, eye tracking, gesture recognition, and touch panels enable hands-free operation.
Applications:
Navigation & Location Services: Real-time GPS overlays enhance situational awareness for pedestrians and drivers.
Workplace Efficiency: Hands-free instructions for industrial workers and real-time data visualization in healthcare and engineering.
Entertainment & Social Interactions: AR gaming, live social media updates, and immersive digital experiences.
2. Smart Hats & Helmets: Advanced Headgear with AI & AR
Smart hats and helmets integrate sensors, displays, and AI to provide enhanced safety, communication, and performance tracking.
Core Features:
Heads-Up Display (HUD): AR overlays provide navigation, notifications, or performance stats directly within the user’s vision.
Brainwave Sensors (EEG): Some smart helmets can analyze brain activity to detect fatigue or improve cognitive training.
Augmented Communication: Built-in microphones and speakers enable voice interaction and real-time communication with teams.
Impact Detection: Sensors monitor external impacts, alerting emergency services in case of accidents.
Use Cases:
Cycling & Motorbike Safety: Real-time navigation, rear-view camera display, and collision alerts.
Construction & Industrial Safety: Heads-up display for workers providing blueprints, instructions, and hazard warnings.
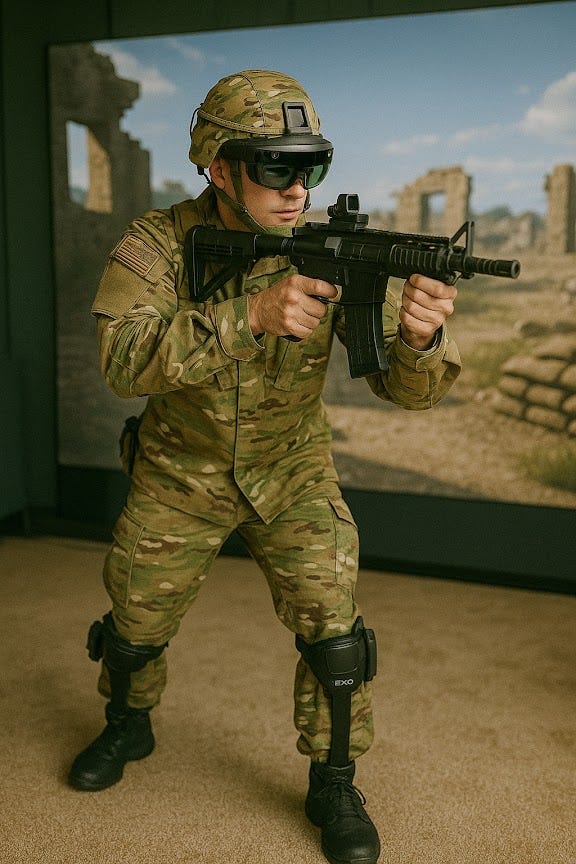
Military & Tactical Operations: Integrated AR for real-time situational awareness, mapping, and enemy detection.
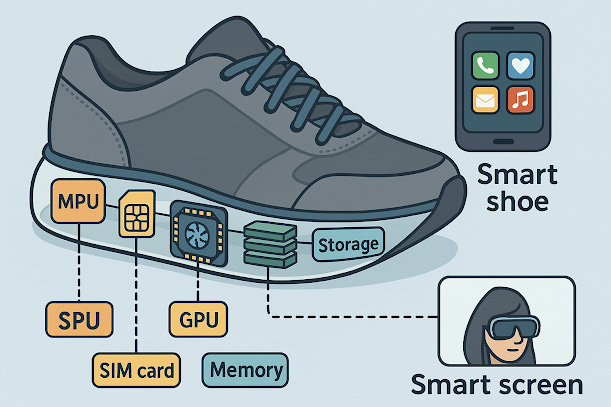
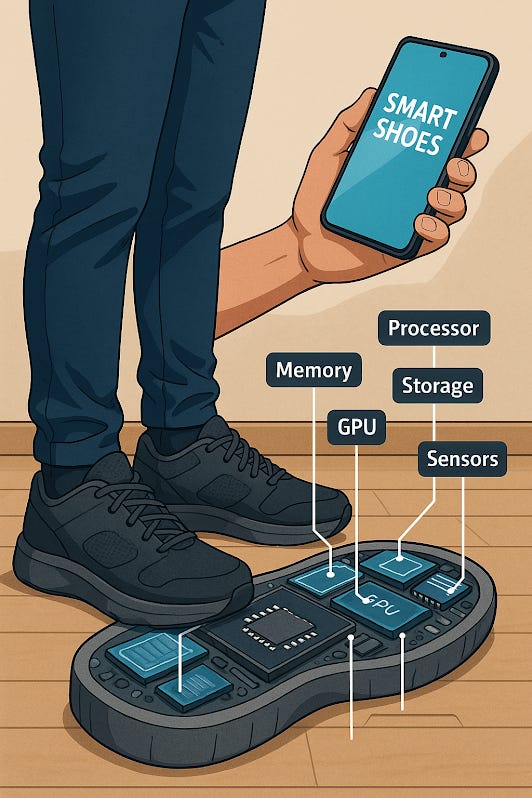
3. Smart Shoes: AI-Powered Mobility and Performance Tracking
Smart shoes incorporate sensors and wireless technology to track movement, provide feedback, and assist users with mobility needs.
Core Components:
Pressure & Motion Sensors: Detect walking patterns, step count, and posture.
Haptic Feedback & Alerts: Vibrations to guide users, especially for navigation assistance.
Self-Lacing Mechanism: Adaptive laces automatically adjust for comfort and support.
Integration with AR Glasses & Smartphones: Displays real-time fitness metrics or navigation guidance.
Use Cases:
Fitness & Athletics: Step analysis, running optimization, and injury prevention.
Navigation for the Visually Impaired: Shoes vibrate to indicate turns or obstacles detected through AI-based navigation.
Medical Applications: Monitoring gait for post-surgery recovery and early detection of mobility disorders.
4. Smart Belts & Braces: Core Body Wearables for Health & Posture
Smart belts and braces enhance health tracking and posture correction using embedded sensors and real-time feedback.
Core Features:
Posture Monitoring: AI-driven analysis detects poor posture and provides corrective feedback.
Health Tracking: Monitors waist circumference changes, heart rate, and hydration levels.
Fall Detection & Emergency Alerts: Detects sudden falls and automatically notifies emergency contacts.
Use Cases:
Fitness & Weight Management: Real-time data analysis helps users track calorie burn and movement efficiency.
Medical & Rehabilitation: Helps patients recovering from spinal injuries maintain correct posture.
Workplace Ergonomics: Prevents back injuries in physically demanding jobs through vibration alerts for incorrect posture.
5. Smart Shoulders: Enhancing Upper Body Functionality
Smart shoulders are an emerging category of wearables designed for posture correction, augmented strength, and health monitoring.
Core Features:
Posture Correction & Ergonomic Support: Monitors shoulder position and provides real-time feedback to reduce strain.
Muscle Fatigue Monitoring: Tracks muscle exertion to prevent injuries during work or sports.
Exoskeleton Support: Some models offer lightweight assistance for physically demanding tasks.
Integrated AI Assistance: Works with other wearables to provide holistic health insights.
Use Cases:
Workplace Assistance: Supports workers in industries requiring repetitive lifting or overhead tasks.
Athletic Training: Helps monitor and improve shoulder positioning in sports like weightlifting and swimming.
Medical & Rehabilitation: Aids recovery from shoulder injuries through guided therapy feedback.
6. The Future of Wearable Integration: A Unified Computing System
The next evolution of smart wearables involves seamless connectivity between devices through a unified computing unit running on a main operating system (OS). This central system allows for:
Cross-Device Synchronization: Smart glasses, hats, shoes, belts, and shoulders communicate in real time to enhance user experience.
AI-Powered Data Processing: A single AI-driven computing core interprets data from multiple wearables to provide a unified, intelligent response.
Cloud Connectivity & Edge Computing: Data processing can occur locally on the device for real-time interaction or be stored and analyzed in the cloud for long-term insights.
Personalized User Experience: Machine learning adapts functionality based on user behavior, providing tailored feedback and automation.
Conclusion
Smart wearables are revolutionizing the way we interact with the world, merging AI, AR, and IoT for an enhanced digital lifestyle. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will not only offer improved functionality and safety but also redefine industries ranging from healthcare to sports and professional work environments. By integrating multiple wearables into a cohesive ecosystem, users can experience a future where technology seamlessly enhances daily life.
The Future of Smart Wearables: Smart Hats, Helmets, and More
Introduction
Wearable technology is evolving beyond smartwatches and AR glasses, introducing an ecosystem of interconnected smart wearables that enhance productivity, health monitoring, safety, and entertainment. Among these advancements, smart hats and helmets are emerging as critical components in various industries, including sports, construction, military, and consumer applications. Paired with smart glasses, smart shoes, smart belts, and other intelligent wearables, they create a seamless, fully immersive digital experience.
1. Smart Hats and Helmets: Augmenting the Headspace
Smart hats and helmets integrate sensors, AR displays, AI, and communication features, offering hands-free interaction and real-time data visualization.
Core Features of Smart Hats & Helmets:
Augmented Reality Integration: Many smart helmets and hats come with AR-compatible visors or head-up displays (HUD) that work alongside AR smart glasses, enhancing navigation, sports performance, and fieldwork.
AI-Powered Voice Assistance: Built-in voice assistants allow users to control devices, take notes, and receive guidance without using their hands.
Health and Safety Monitoring: Embedded sensors track body temperature, hydration levels, and stress levels, alerting users to potential health risks.
Bone-Conduction Audio: These devices use bone-conduction technology to provide audio feedback while keeping the ears free for situational awareness.
Impact Detection and Emergency Alerts: In high-risk jobs like construction or cycling, smart helmets can detect falls and automatically send distress signals to emergency contacts.
Smart Cooling and Heating: Some helmets feature temperature regulation systems to adapt to extreme weather conditions.
Use Cases of Smart Hats & Helmets:
Cycling & Motorcycling: AR helmets provide real-time speed, route navigation, and weather updates.
Construction & Industrial Safety: Workers benefit from HUD overlays for blueprints, safety instructions, and emergency alerts.
Military & Tactical Use: Soldiers use AR-integrated smart helmets for battlefield awareness, communication, and real-time drone feed displays.
Athletics & Training: Smart hats for runners and athletes provide biometric tracking, form correction, and performance analytics.
2. Interconnectivity with Other Smart Wearables
The true potential of smart hats and helmets is unlocked when they interact with other smart wearables such as AR glasses, smart shoes, smart belts, smart bracelets, and touchscreen devices.
Smart Glasses & Smart Hats: The Perfect Pair
Smart hats can act as a power source or additional sensor hub for AR glasses, extending battery life and enhancing spatial awareness.
Built-in eye-tracking in smart helmets can enhance AR glasses’ interaction, enabling seamless control with just an eye movement.
Smart Shoes: Step Into the Future
Gait Analysis & Posture Correction: Smart shoes analyze walking patterns and send real-time feedback to the smart hat for posture improvements.
Navigation Enhancement: AR glasses can display directional overlays guided by real-time location tracking from smart shoes.
Adaptive Support: Smart shoes can adjust cushioning based on the user's activity (e.g., running, standing, or hiking).
Smart Belts: The Intelligent Core
Posture Monitoring: Smart belts can track core stability and alert users when their posture is incorrect.
Health Insights: They measure abdominal pressure, breathing patterns, and hydration levels.
Power Hub: Some smart belts double as a charging dock for AR glasses, smart hats, and other wearables, ensuring extended usage.
Smart Bracelets & Wearable Controllers
Gesture Control: Wearable controllers on the wrist enable users to interact with AR interfaces using hand gestures.
Health & Fitness Tracking: Smart bracelets monitor vitals, including heart rate and oxygen levels, syncing with the smart hat’s biometric sensors.
Haptic Feedback: Provides physical feedback to enhance immersive AR experiences in gaming, sports, and workplace applications.
3. Smart Wearables in Different Industries
Sports & Fitness
Smart hats for athletes measure sweat levels, hydration, and concussion impact.
Smart shoes enhance training by adjusting resistance and providing real-time feedback.
Smart belts track posture, core strength, and breathing.
Healthcare & Wellness
Smart hats monitor neurological activity and can detect early signs of fatigue or cognitive decline.
Smart belts provide fall detection for the elderly and alert caregivers in emergencies.
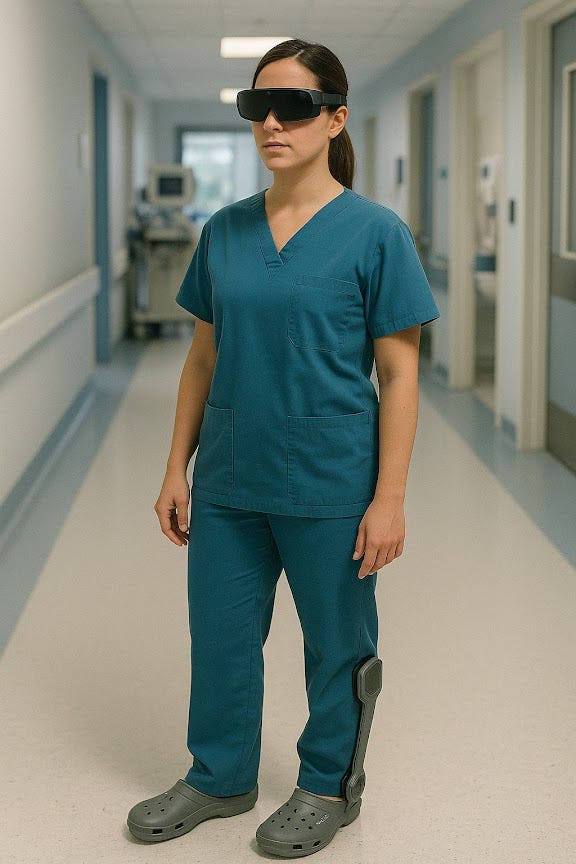
Smart glasses & AR assist doctors by overlaying patient data during surgeries.
Workplace & Industry
AR helmets & glasses improve efficiency by displaying schematics and instructions hands-free.
Smart belts prevent injuries by monitoring lumbar strain.
Smart shoes enhance workplace safety by detecting hazards and alerting users.
Military & Defense
Smart helmets display battlefield data with night vision and real-time tactical insights.
Smart belts track soldier vitals and detect injuries.
AR glasses provide navigation and enemy tracking.
Retail & Customer Experience
Smart hats in fashion integrate LED displays and customizable designs.
Smart belts and accessories enable hands-free shopping experiences with AR-enhanced product information.
4. Challenges & Future Prospects
Challenges:
Battery Life: High-performance smart wearables require efficient power management.
Data Privacy & Security: With multiple devices collecting biometric data, cybersecurity risks must be addressed.
User Comfort & Style: Smart wearables must be lightweight and aesthetically appealing to encourage adoption.
Future Developments:
AI-Enhanced Wearables: AI-driven features will enhance automation, personalization, and predictive analysis.
5G & Cloud Connectivity: Faster data processing will enable seamless interaction between wearables.
Flexible, Wearable Tech: Innovations in smart fabric will integrate technology into everyday clothing.
Conclusion
Smart hats, helmets, and other intelligent wearables are shaping the future of augmented reality, health monitoring, and hands-free computing. As these devices continue to evolve, they will form an interconnected network, seamlessly blending the digital and physical worlds. The integration of smart shoes, smart belts, AR glasses, and AI-driven technologies promises a revolution in human-computer interaction, enhancing every aspect of daily life, from sports and work to entertainment and health.
Biometric Personalization in Smart Wearables
As wearable technology continues to advance, one of the most powerful features is the ability to create biometric profiles that enable seamless, highly personalized experiences. These profiles are created through the continuous monitoring of a user's physiological and behavioral data, which is then analyzed and acted upon by the wearables. The more accurate and holistic the data, the more customized the system’s responses, improving everything from comfort to performance.
1. Biometric Data Collection
Smart wearables, such as AR glasses, smart hats, smart shoes, and smart belts, will be equipped with a range of sensors designed to capture various forms of biometric data. These devices will continuously monitor, analyze, and adapt to a user’s physical and emotional state by collecting:
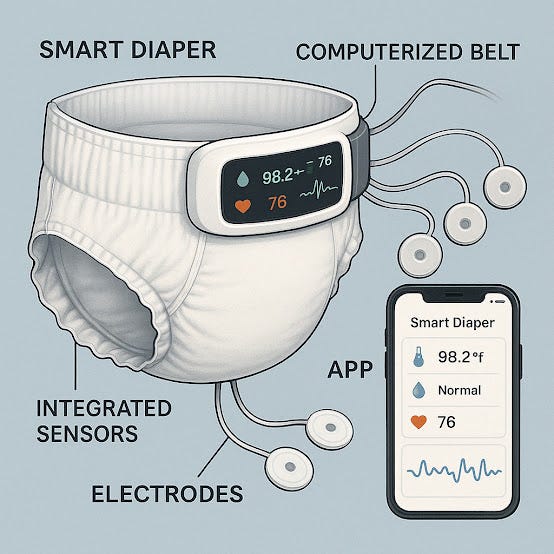
Heart rate and heart rate variability: Monitored through sensors in belts, shoes, or wristbands, providing insights into stress, recovery, and overall cardiovascular health.
Temperature sensors: Embedded in clothing, hats, or shoes to monitor body temperature and adjust environmental settings or offer feedback on user wellness.
Motion and Gait Analysis: Sensors in shoes or smart pants that track the user’s gait, stride, and movement patterns, adjusting accordingly to promote better posture and physical alignment.
Brainwave Activity: Detected by helmets or headgear, this can measure levels of concentration, fatigue, and even cognitive performance.
Skin Conductivity: Embedded into smart fabrics or wearables, this can help track emotional responses, such as stress or relaxation, by measuring sweat levels or skin response.

2. AI-Powered Biometric Profiles
The data collected by these wearables is processed by a centralized AI engine that creates a unique biometric profile for each user. This AI doesn’t just record the data—it interprets it and adapts to the user’s lifestyle, preferences, and behaviors over time. Here's how this works:
Learning Patterns: The more a user wears the devices, the more the system learns about their habits and needs. Over time, the AI understands when the user is most active, stressed, or needs rest. For example, the system might automatically adjust the user’s fitness routine based on their muscle fatigue detected through smart shoes or suggest more relaxing activities if their heart rate variability indicates high stress.
Personalized Feedback & Adjustments: The AI can send alerts or notifications based on the biometric data, such as recommending hydration when sweat levels are too high or suggesting a break if prolonged stress is detected. It may also adjust environmental factors, like adjusting the temperature of the smart hat or suggesting adjustments to posture through the smart belt.
Dynamic Health Monitoring: In the context of healthcare, this biometric system could offer real-time tracking of critical parameters, alerting users and healthcare providers to potential issues before they become critical. For example, a sudden change in a user’s heart rate or blood oxygen level could trigger an emergency alert to medical personnel or prompt the wearable to adjust the user's activity accordingly.
3. Biometric Authentication & Security
Beyond health and performance, biometric wearables also offer advanced security features, ensuring that only the user can access the device or the data it holds. Here’s how biometric authentication could work:
Multimodal Authentication: Devices could combine several forms of biometric data for enhanced security. This includes:
Facial recognition through embedded cameras in AR glasses or helmets.
Fingerprint scanning through smart rings, belts, or smart gloves.
Voice recognition through the integration of microphones and AI voice assistants embedded in wearables.
Gait and motion biometrics captured by the shoes or lower body sensors. The way you walk could be used to verify your identity, just like a fingerprint.
Biometric Payment Systems: Your wearables could also support biometric payments, allowing you to make secure transactions with just a touch or glance. This could extend to things like paying for public transport with your smart shoes or making purchases with a quick scan of your AR glasses.
4. Emotional Intelligence & Cognitive Monitoring
Smart wearables can track more than just physical metrics—they can monitor emotional and cognitive states too. By assessing heart rate variability, sweat levels, skin conductivity, and brainwave activity, wearables can gain insights into a user’s mood and mental health. This is particularly relevant for mental well-being:
Stress Detection: By monitoring physiological responses to stress (like increased heart rate or sweat levels), the system could provide immediate suggestions to manage stress, such as recommending breathing exercises, suggesting a break, or adjusting the environmental settings (like lighting or sound) to help the user relax.
Focus and Productivity: Devices like AR glasses or smart helmets could track a user’s cognitive load, providing insights into when someone might be nearing mental fatigue or a need for a break, offering adjustments to optimize mental performance.
Real-time Emotional Support: Wearables could integrate with virtual assistants to provide emotional support, such as motivational messages, breathing exercises, or even adjusting your music or ambient lighting based on your emotional state. This AI-driven emotional intelligence could be crucial in industries like customer service or healthcare, where managing emotions and mental health is critical.
5. Full Integration Across Wearables
The true magic of these biometric wearables lies in their full integration within a larger ecosystem. All wearables—whether it’s a smart hat, AR glasses, shoes, belt, or braces—will be able to sync data in real-time to a centralized computing system that serves as the brain of the operation. This system will not only ensure data flows seamlessly but will enable wearables to function as a cohesive unit, offering a truly personalized experience. For example:
Smart Hat + AR Glasses: The hat could collect biometric data related to brain activity, while AR glasses provide real-time situational feedback based on the cognitive load detected by the smart hat.
Smart Shoes + Smart Belt: Shoes monitor your movement efficiency and posture, while the belt ensures optimal alignment of your core, offering feedback based on real-time analysis from both devices.
Smart Shoulders + Smart Braces: These wearables monitor upper body posture and muscle strain, coordinating with the smart belt to ensure an overall ergonomic and injury-free user experience.
Conclusion
Biometric personalization is at the core of the next generation of smart wearables. These devices not only monitor our physical and emotional states but also adapt and respond to our needs in real-time. By combining advanced AI algorithms with powerful biometric data collection, wearables can offer customized experiences that enhance our well-being, improve our performance, and protect our health. This integration of personalized technology will open up new possibilities for how we live, work, and interact with the world around us, with wearables becoming an extension of our own biological systems.
Would you like to go deeper into any specific aspect of these biometric capabilities or explore potential use cases in more detail?
Biometric Smart Wearables in Different Sectors
1. Work: Enhancing Productivity and Safety
In professional settings, biometric smart wearables can vastly improve productivity, well-being, and workplace safety. Here’s how:
Personalized Work Environment:
Smart glasses with augmented reality (AR) can overlay real-time data, instructions, and notifications during a workday. For instance, engineers or assembly line workers can see step-by-step instructions right in front of them, without needing to look away from their tasks.
Smart belts and braces provide real-time feedback on posture and body alignment, ensuring workers maintain optimal ergonomics, preventing long-term injury. These can be essential in manual labor-heavy jobs or professions requiring sustained physical activity.
Biometric Stress and Fatigue Monitoring:
Smart shoes or belts could monitor physical activity and provide insights into energy levels or fatigue, alerting the user when it’s time for a break or suggesting relaxation exercises to prevent burnout.
Heart rate variability (HRV) and brainwave activity tracking through wearable headgear or bands can offer valuable insights into emotional stress, allowing employers or employees to take proactive measures to improve mental well-being. Personalized alerts could notify the user when they are under stress and suggest relaxation or mindfulness exercises.
Collaboration and Communication:
Wearables like smart hats or smart glasses with voice assistants and gesture control can enhance communication, especially for remote workers or those in fields requiring hands-free operation. For example, a surgeon performing surgery could interact with their AR glasses to receive real-time data and updates without having to pause the procedure.
The AI-driven assistant in these wearables could filter information and prioritize messages based on urgency, helping workers maintain focus.
2. Aviation: Maximizing Safety, Precision, and Performance
Aviation is an industry where safety and precision are paramount, and biometric smart wearables can significantly enhance both.
Pilot Health Monitoring:
Smart helmets or headgear integrated with biometric sensors can monitor a pilot’s heart rate, brainwaves, and fatigue levels. In a high-stress environment like aviation, these wearables can prevent accidents by alerting the pilot to physical or mental fatigue, ensuring timely breaks are taken to maintain peak performance.
Stress and cognitive load can be managed by monitoring the brainwave activity, ensuring pilots stay calm and focused during high-pressure situations.
Smart Communication in Cockpits:
AR smart glasses could provide pilots with critical data overlayed in their field of vision—altitude, speed, weather conditions, and navigation data—allowing them to focus entirely on flying the plane without looking away from the controls.
Wearables can track reaction times and provide feedback on mental readiness, helping pilots remain sharp throughout long flights.
Flight Crew Wellness:
Smart belts and posture-correcting wearables can ensure that cabin crew maintain proper posture, especially during long shifts that may involve standing or walking for extended periods.
Biometric sensors can track hydration levels, preventing dehydration in environments like aircraft cabins, where humidity levels are typically low.
3. Life: Enhancing Everyday Health, Well-Being, and Convenience
In daily life, smart wearables can dramatically improve overall well-being, personal health, and convenience.
Personalized Health Monitoring:
Devices like smart hats, glasses, and shoes can monitor biometrics continuously throughout the day. Heart rate, step count, calorie burn, and sleep patterns are just the beginning. By tracking multiple factors simultaneously, wearables can give users an in-depth understanding of their body’s needs and how to respond.
For instance, a smart shoe might recommend more balanced walking patterns if the system detects an unusual gait, reducing the risk of injury.
Preventative Healthcare:
Wearable sensors integrated with AI can predict health issues before they occur. For example, detecting a potential heart condition through irregular heartbeats or noticing high stress levels through consistent biometric readings could trigger a health check-up reminder.
Smart belts with posture correction could alert the user when they are slouching or when their posture could lead to neck or back pain, offering gentle reminders to straighten up.
Emotion-Based Feedback:
Through continuous tracking of emotional states via sensors (e.g., heart rate, skin conductivity), the system can suggest coping strategies in moments of stress, such as relaxation techniques, breathing exercises, or even mood-boosting playlists.
4. Gaming: Immersive, Personalized Experiences
In the realm of gaming, smart wearables can take immersion to new heights by incorporating biometric data and physical responses into the gaming experience.
Enhanced Immersion:
AR glasses or headsets can overlay in-game data directly into the player’s field of vision, offering a more immersive experience where the game world interacts directly with real-world movements and responses.
Smart shoes and smart belts could track a gamer’s physical movements and apply them in real-time to the game environment. For instance, a player's walking or running in the real world could be mirrored as movement in the game, while haptic feedback in the shoes or gloves could simulate the feeling of walking on different terrains or encountering in-game obstacles.
Physical Performance Monitoring:
Wearables like smart shoes could track a gamer’s reaction times, physical endurance, and gait efficiency, providing valuable feedback on physical readiness during long gaming sessions.
Smart headsets could monitor brain activity and focus levels, offering insights into the player's concentration and mental state, helping them optimize gaming strategies or take breaks to prevent fatigue.
Behavioral Analytics:
In multiplayer settings, wearables could provide real-time insights into players’ emotional responses, such as frustration or excitement, using data from skin conductance and heart rate variability. This data could then be used to adjust the game’s difficulty level or trigger personalized in-game events based on the player's emotional state.
Fitness Gaming:
Smart wearables can combine gaming with fitness. For example, fitness-based games can track the player’s caloric burn, muscle engagement, or fatigue levels through biometric sensors, motivating them to stay active and improve their fitness while having fun.
Conclusion: The Transformative Power of Biometric Smart Wearables
From improving workplace productivity, aviation safety, and personal health to enhancing gaming immersion and performance, biometric smart wearables are reshaping how we interact with the world and ourselves. By combining AI, augmented reality, and biometric sensors, these wearables offer personalized, real-time feedback, enhancing the user experience across various domains.
Whether it’s ensuring a pilot stays mentally sharp during a long flight, a gamer has a truly immersive experience, or a worker receives proactive health alerts, smart wearables are becoming indispensable tools for optimizing health, performance, and safety in modern life.
Would you like to delve deeper into any of these applications or explore potential challenges in integrating such technologies into these sectors?
Here's a technical article focusing on biometric smart wearables and their integration in different sectors such as work, aviation, life, and gaming.
Biometric Smart Wearables: Technical Insights and Applications in Key Sectors
Introduction
The integration of biometric smart wearables into daily life represents a major leap forward in wearable technology, offering continuous real-time monitoring and advanced data analytics. These devices—encompassing smart hats, smart shoes, AR glasses, smart belts, and biometric sensors—are designed to not only provide a personalized user experience but also gather crucial data on physiological and psychological states. Their applications span multiple industries, revolutionizing work environments, aviation safety, personal health, and even gaming experiences.
1. Core Components of Biometric Smart Wearables
Biometric smart wearables are equipped with a variety of sensors and connectivity protocols to enable real-time data processing and cross-device synchronization. The key technologies driving these devices include:
Biometric Sensors:
Heart Rate Sensors (ECG, PPG): These sensors track heart rate variability, which provides insight into stress, fatigue, and overall cardiovascular health.
Brainwave Sensors (EEG): Used in smart hats and helmets, EEG sensors track brain activity, allowing for fatigue detection, cognitive load analysis, and personalized feedback on mental wellness.
Motion and Gait Sensors (Accelerometers, Gyroscopes): These sensors monitor body movements, providing data on posture, gait, and physical activity, essential for smart shoes and belts.
Skin Conductance Sensors: Used to detect emotional stress and monitor autonomic responses, these sensors are vital for detecting emotional states in both professional and gaming environments.
Connectivity Protocols:
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): A key communication protocol, BLE allows for energy-efficient data transfer between wearables and a central computing unit or mobile device.
Wi-Fi and 5G Connectivity: For real-time data streaming and cloud integration, smart wearables leverage Wi-Fi or 5G networks to sync with remote servers or other connected devices, enabling instant feedback and updates.
Edge Computing: Edge computing allows for local data processing on the wearables themselves, reducing latency and enabling quicker decision-making. For example, a smart helmet may use edge processing to immediately alert the user of fatigue or impact, ensuring timely intervention.
Power Management:
Energy Harvesting and Batteries: Wearables rely on advanced energy-harvesting technologies (e.g., kinetic energy or thermoelectric generators) to maintain battery life. Additionally, low-power circuits and optimized battery management ensure extended device usage without frequent recharging.
2. Application of Biometric Smart Wearables in Key Sectors
Work: Enhancing Productivity and Safety
In professional environments, biometric wearables enhance productivity, physical health, and safety by providing continuous feedback on performance and well-being.
Smart Glasses and AR Integration:
Augmented Reality (AR) plays a central role in improving productivity by overlaying real-time information directly into the user’s field of vision. For instance, engineers can use smart glasses to access step-by-step instructions or safety data while keeping their hands free for work.
Gesture and Voice Control: These wearables employ gesture recognition and voice commands to allow users to interact with digital interfaces without physically touching a device, streamlining workflows in high-intensity or hands-on environments.
Health and Wellness Monitoring:
Smart belts and braces continuously monitor posture and body alignment, sending real-time feedback to users. This is crucial for those working in manual labor jobs or sedentary office environments where poor posture can lead to long-term health issues.
Stress and Fatigue Detection: Wearables equipped with heart rate variability (HRV) sensors and brainwave monitors can assess mental fatigue and stress levels. The system can send alerts to employees when performance may be impacted due to fatigue, ensuring timely breaks and reducing the risk of burnout.
Safety Monitoring:
Smart helmets and hard hats can detect impact or falls and immediately send alerts to supervisors or emergency responders, helping mitigate the consequences of accidents on-site.
3. Aviation: Ensuring Safety, Cognitive Performance, and Physical Health
Aviation demands the highest level of safety, mental focus, and physical health, and wearable biometric devices can improve operational efficiency in this high-stakes environment.
Cognitive Load Monitoring:
EEG sensors integrated into smart helmets or headsets allow for continuous monitoring of the pilot's cognitive load and mental fatigue. Real-time data analysis can detect mental exhaustion or distraction, which could compromise flight performance.
Alerts can be generated to advise pilots when it’s time for a mental or physical break to ensure optimal cognitive function throughout the flight.
Health Monitoring for Crew:
Heart rate and hydration levels are continuously monitored, ensuring that pilots and crew members remain in optimal health. Dehydration or overexertion can affect cognitive performance, and continuous monitoring helps avoid such risks.
Motion sensors in smart shoes can track the crew’s movement and provide feedback on their activity levels to prevent fatigue, particularly on long-haul flights.
In-Flight Data Synchronization:
Wearables can sync flight data with the aircraft's onboard systems, providing real-time metrics about pilot performance, aircraft status, and cabin conditions. This synchronization enables improved decision-making and overall flight management.
4. Life: Optimizing Daily Activities and Preventative Health
In everyday life, biometric wearables offer personalized insights into health and well-being, leading to proactive decision-making and enhanced quality of life.
Posture and Gait Monitoring:
Smart shoes and smart belts provide data on how a person walks, helping to detect issues like poor gait patterns or musculoskeletal imbalances. This is particularly useful in preventing chronic pain and improving mobility, especially for individuals recovering from injuries.
Posture correction is a key feature, with smart belts alerting the user to slouching and offering real-time feedback to adjust posture.
Health Insights for Chronic Conditions:
Wearables that monitor vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and blood oxygen levels can help manage chronic conditions such as hypertension or diabetes. Personalized health suggestions and alerts are generated based on this data, promoting early intervention and better self-management of health.
Emotional and Stress Monitoring:
Devices with skin conductance or heart rate variability sensors can detect emotional states such as stress, anxiety, or relaxation. Using this data, wearables can suggest tailored coping strategies or mindfulness techniques, providing users with insights into their mental well-being.
5. Gaming: Merging Physical and Virtual Realities
In the gaming sector, biometric wearables provide deeper immersion and create interactive experiences that respond to physical and emotional states.
Movement-Based Gameplay:
Smart shoes and motion sensors detect real-world movements and translate them into virtual gameplay. For instance, a player running in real life could be made to run faster or slower in the game based on their real-world pace.
Haptic feedback in smart shoes or gloves adds another layer of immersion by simulating physical sensations (e.g., walking on different terrains, feeling in-game impacts).
Emotional Feedback and Adaptive Gaming:
Emotion sensors can track a player's level of stress or excitement during a gaming session. This data can be used to dynamically adjust the game’s difficulty or environment to provide a more personalized and engaging experience.
Brainwave monitoring via smart headgear allows the system to detect focus levels, ensuring that the player is fully immersed and engaged.
Conclusion
Biometric smart wearables offer transformative potential across various sectors, from improving workplace productivity and aviation safety to optimizing personal health and gaming immersion. With advancements in biometric sensors, AI-powered analytics, and real-time connectivity, these wearables provide not only a personalized user experience but also continuous monitoring for safety, performance, and well-being.
The integration of these devices with centralized computing systems and cloud or edge technologies ensures seamless data synchronization and intelligent decision-making, paving the way for more efficient, safe, and responsive environments in both professional and personal spheres.
Biometric Smart Wearables: Integration with Smart Homes, Vehicles, Healthcare, Education, and Everyday Life
Introduction
As the demand for smart technology increases, biometric smart wearables are becoming essential components that drive the evolution of modern smart homes, smart vehicles, healthcare systems, education, and general daily life. By integrating advanced sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time connectivity, these devices enable seamless interactions between individuals and their environment. Whether it’s monitoring health metrics in hospitals, enhancing learning experiences in classrooms, or optimizing the functionality of smart homes and vehicles, biometric wearables serve as the next frontier of intelligent, connected living.
In this article, we will explore how biometric smart wearables can revolutionize these sectors and provide tangible benefits to individuals, industries, and society.
1. Biometric Smart Wearables in Smart Homes
Smart homes are rapidly evolving into intelligent ecosystems that anticipate and respond to the needs of their occupants. Biometric smart wearables can significantly enhance this experience by enabling more personalized and secure interactions with home devices.
Personalized Environment Control
Smart thermostats, lighting, and entertainment systems can be controlled through biometric feedback. For example, a smart hat or glasses could detect the user’s body temperature and adjust the home’s climate automatically. Similarly, smart shoes could monitor the user’s movement patterns, adjusting lighting intensity based on room occupancy or activity levels.
Security and Authentication
Biometric authentication via fingerprints, voice recognition, or face scanning through smart wearables can be used to secure access to homes and other areas. These wearables can communicate with smart locks or security systems, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access certain areas.
Health Monitoring for Personalized Care
Continuous monitoring of vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, blood oxygen levels) from smart belts, shoes, and AR glasses can provide real-time health updates. This data can be sent to healthcare providers or caregivers, offering a proactive approach to healthcare and ensuring timely intervention when necessary.
2. Biometric Smart Wearables in Smart Vehicles
As the automotive industry transitions toward autonomous vehicles and connected transportation systems, biometric smart wearables play a key role in enhancing safety, comfort, and the overall driving experience.
Driver Health and Alertness Monitoring
Smart wearables equipped with EEG sensors and heart rate monitors can track the driver’s alertness, stress levels, and fatigue. These devices can communicate with the vehicle’s driver assistance systems (ADAS) to issue alerts when the driver is drowsy or distracted, helping prevent accidents caused by inattention.
Personalized Driving Experience
Integration with smart vehicles allows wearables to adjust the vehicle settings based on personal biometric data. For example, the car’s seating position, climate controls, or infotainment system could be automatically customized for the driver’s preferences based on physiological feedback from a smart belt or glasses.
Occupant Safety
Biometric sensors can also be integrated into the vehicle’s safety features, such as seatbelts and airbags, to assess the passenger’s health in case of an accident. Smart helmets and shoes can detect signs of injury or distress, automatically notifying emergency services for a quicker response.
3. Biometric Smart Wearables in Healthcare and Hospitals
Biometric wearables have the potential to revolutionize healthcare by providing continuous, real-time health monitoring, reducing hospital readmissions, and improving patient outcomes.
Remote Health Monitoring and Telemedicine
Smart wearables allow healthcare providers to monitor patients' vital signs, including heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood oxygen levels. Smart belts, shoes, and hats can detect abnormal conditions, like heart arrhythmias or postural issues, sending alerts to both patients and healthcare providers.
Chronic Condition Management
For patients with chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea, biometric wearables provide consistent monitoring, ensuring that treatment plans are followed and that physicians have up-to-date data on their patients' conditions. Smart shoes can help diabetic patients monitor their gait and foot health, preventing injuries or complications.
In-Hospital Patient Monitoring
Wearables integrated with hospital systems can track patient mobility, positioning, and safety. For example, smart braces can detect falls, alerting medical staff immediately. Wearables can also be used to monitor the patient’s level of pain, fatigue, or alertness, aiding healthcare professionals in providing better, more personalized care.
4. Biometric Smart Wearables in Education
In the realm of education, biometric wearables provide valuable tools for enhancing learning experiences, monitoring student well-being, and improving academic performance.
Student Health and Well-being
Smart wearables can monitor students' stress levels, focus, and emotional states during study or exams. This data helps educators understand when students are overwhelmed or disengaged, enabling tailored interventions to improve learning outcomes.
Performance Tracking in Physical Education
Smart shoes, belts, and wristbands can be used to track physical activity during sports or gym classes. Wearables can measure heart rate, distance traveled, and calories burned, helping instructors assess students' physical fitness and guide them toward healthy goals.
Focus and Engagement Monitoring
EEG and motion sensors embedded in smart hats or glasses can detect a student's level of focus during lectures. These data points can be used to adapt the learning environment, adjusting lecture pace, providing additional resources, or incorporating interactive activities to keep students engaged.
5. Biometric Smart Wearables in Everyday Life
Biometric smart wearables offer profound benefits in everyday life by enabling a more connected, intelligent, and personalized experience in various activities.
Fitness and Activity Monitoring
Smart shoes and fitness bands offer in-depth tracking of physical activities such as running, walking, and cycling. These devices monitor steps taken, calories burned, and distance covered, providing feedback to help users improve their fitness levels.
Sleep Monitoring and Improvement
Smart wearables like smart hats or glasses are capable of tracking sleep patterns, providing insights into sleep stages, restlessness, and quality of sleep. Personalized feedback is then offered to help users improve their sleep hygiene and overall health.
Mental Health and Stress Management
Using skin conductance and heart rate variability sensors, wearables can detect stress or anxiety levels throughout the day. This data can trigger personalized relaxation techniques or suggest mindfulness exercises to alleviate emotional tension, contributing to better mental health management.
6. The Role of Centralized Computing Systems
All the wearables discussed above operate as part of a connected ecosystem, communicating with each other and integrating into centralized computing systems. These systems enable:
Cross-Device Synchronization: Biometric wearables from various manufacturers can communicate with one another, sharing health, performance, and contextual data in real-time.
AI-Powered Analytics: Data from wearables is aggregated and analyzed to provide personalized feedback and predict health trends, ensuring users can make informed decisions about their well-being.
Cloud and Edge Computing: Wearables store critical data either locally or in the cloud, ensuring real-time analysis, data storage, and system integration across different platforms, enabling the device to function intelligently without excessive lag or delays.
Conclusion
Biometric smart wearables are transforming how we interact with our environments, improving safety, productivity, and well-being in diverse sectors such as smart homes, smart vehicles, healthcare, education, and everyday life. The integration of biometric sensors, AI-driven analytics, and real-time connectivity empowers users with more personalized experiences and actionable insights. As these devices continue to evolve and become more integrated into daily routines, they will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of connected living.
The Future of Digital Augmented Virtual Reality Tech in Wearable Sports and Security Equipment
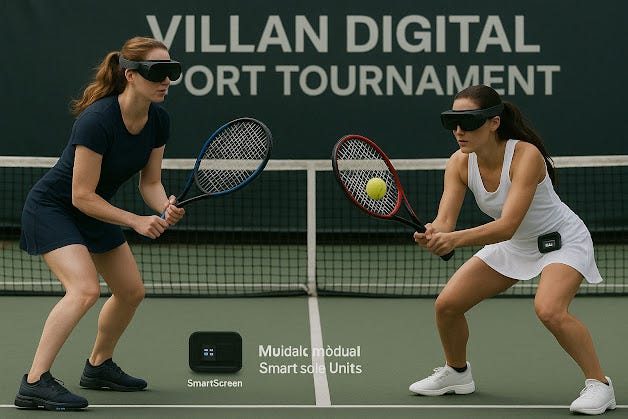
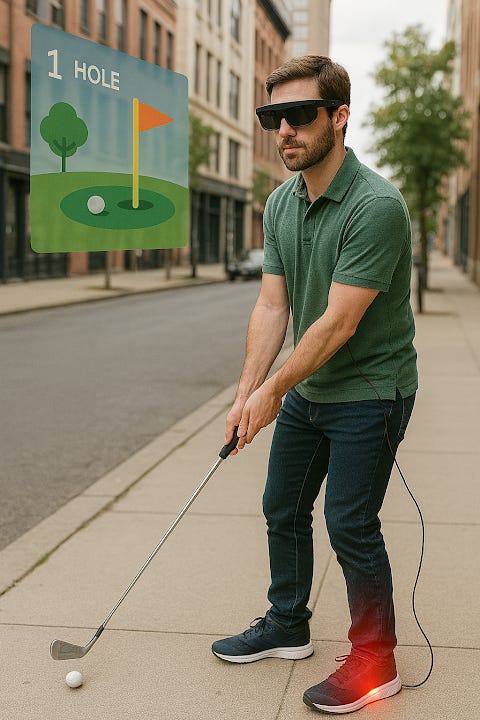
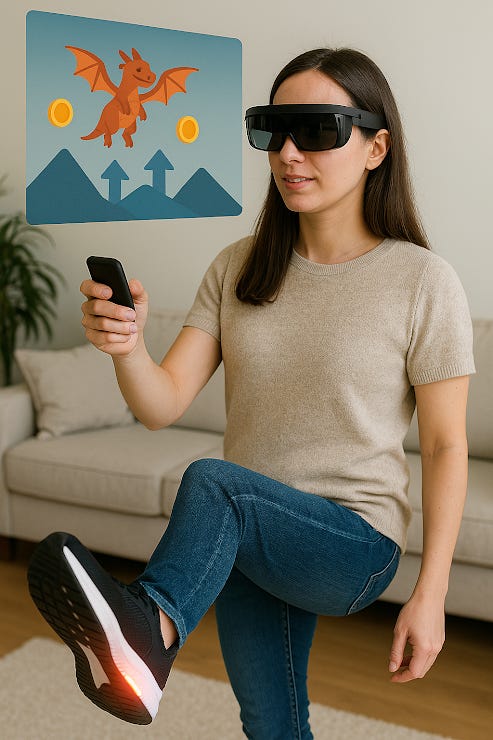
The convergence of wearable technology and augmented reality (AR) is setting the stage for a new era in sports, security, military operations, and personal health. Imagine being able to play a round of golf or football, not in a traditional sense, but in a fully immersive Digital Augmented Virtual Reality (DAVR) environment. With a simple combination of smart glasses, smart shoes, and smart hats, players can engage in these activities like never before, blending physical performance with digital enhancement for training, entertainment, or competition.
1. The Role of Smart Wearables in Augmented Reality Sports
The future of sports and fitness will be driven by smart wearable devices that enhance physical performance through real-time data and interaction with virtual environments. These devices will include:Smart Glasses: Equipped with AR displays, they project digital images directly into the player’s line of sight. Whether it’s a real-time overlay of the football field or enhanced data showing trajectory for golf shots, smart glasses will allow players to interact with their environment in novel ways.Smart Shoes: Embedded with sensors and haptic feedback technology, these shoes track movement, measure impact, and offer real-time guidance. For example, in football, they can measure stride length, running speed, and agility, while in golf, they can analyze posture and swing mechanics. Through augmented reality, they can overlay a visual path on the ground to guide the user toward an ideal shot or movement.Smart Hats: These can monitor cognitive load, fatigue, and even help with game strategy. In sports, hats could provide real-time stats and feedback, or even offer cool down or alert mechanisms to optimize player safety.These devices combine to create a fully immersive AR sports experience, where athletes can participate in virtual tournaments, test their skills, and track their improvements in an environment that adjusts to their level.
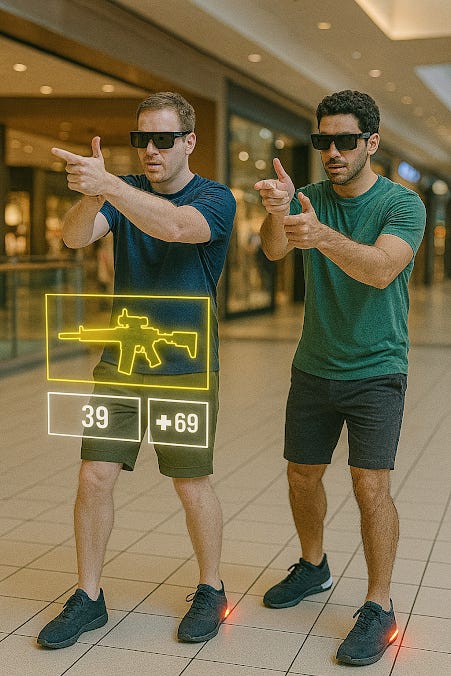
2. Enhancing Security and Military Operations with Wearable AR Tech
The same technology that powers sports simulations can be adapted for critical fields such as law enforcement and military operations:Smart Glasses for Police Forces: In a law enforcement context, AR glasses can enhance situational awareness. Equipped with face recognition software, the glasses can identify suspects, access criminal records, and provide real-time alerts to officers, improving the speed and accuracy of their decision-making. This could be particularly useful in crowded public spaces or high-stakes environments where identifying a person quickly is crucial for public safety.Military Wearables for War Simulators: For military forces, AR glasses can integrate with digital war simulators, providing soldiers with real-time intelligence, battlefield maps, and tactical overlays while on missions. Smart shoes and smart hats can offer biomechanical feedback, ensuring that soldiers are not overexerting themselves while performing physically demanding tasks. This integration of AR in training scenarios could simulate battlefield environments, providing soldiers with realistic scenarios without the need for a live battlefield.
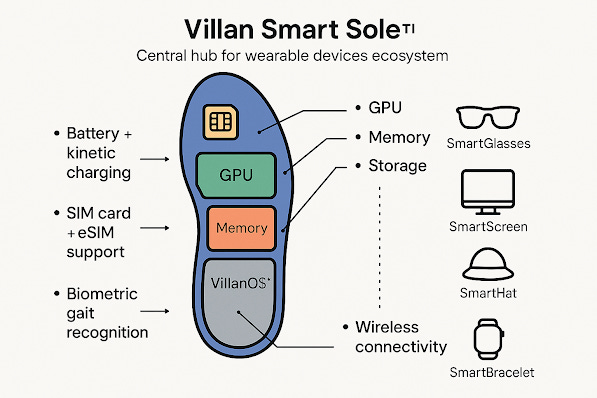
3. The Role of Smart Soles and Other Wearables in Augmented Reality
The smart soles for shoes, in particular, are a game-changer. These advanced soles will combine biometric data collection with augmented reality features to enhance both physical performance and the user experience. The soles can:Track foot movement, pressure, and gait.Provide haptic feedback to guide users through various physical tasks, such as sports training or fitness routines.Integrate with other wearable devices to offer a comprehensive feedback loop, enhancing accuracy and engagement in sports and physical activities.Other wearables, including smart shirts, smart belts, smart gloves, and smart watches, can also play an essential role in this ecosystem. They will combine with the smart soles, shoes, glasses, and hats to create a seamlessly connected system. This system can help athletes, soldiers, and law enforcement personnel reach peak performance, safety, and accuracy.
4. The Future Impact and Opportunities
The integration of smart wearables with augmented reality technology offers transformative potential across various sectors:Sports Training: With AR, athletes can create personalized training environments, simulate complex scenarios, and receive real-time performance data. This will not only enhance training but also allow for advanced performance analysis.Security & Military: Smart wearables can improve operational efficiency and safety, providing law enforcement and military personnel with enhanced situational awareness, faster decision-making capabilities, and an integrated understanding of their environment.Healthcare: In hospitals or rehabilitation centers, wearables can be used to monitor patient health, track recovery progress, and ensure that interventions are tailored to the individual’s needs, enhancing the patient experience.Gaming and Entertainment: Augmented reality gaming could reach unprecedented levels of immersion, allowing users to participate in physical activities like running, cycling, or even playing sports while interacting with a virtual world.
Conclusion
The rise of digital augmented virtual reality technologies integrated with smart wearables is reshaping industries and everyday life. Whether in sports, security, military, or healthcare, these innovations are creating a new era of personalized, data-driven, and immersive experiences. With advancements in AI, biometric sensors, and real-time connectivity, the future is one where wearable tech not only enhances performance and safety but also improves the way we interact with our environments, unlocking endless possibilities for both personal and professional growth.
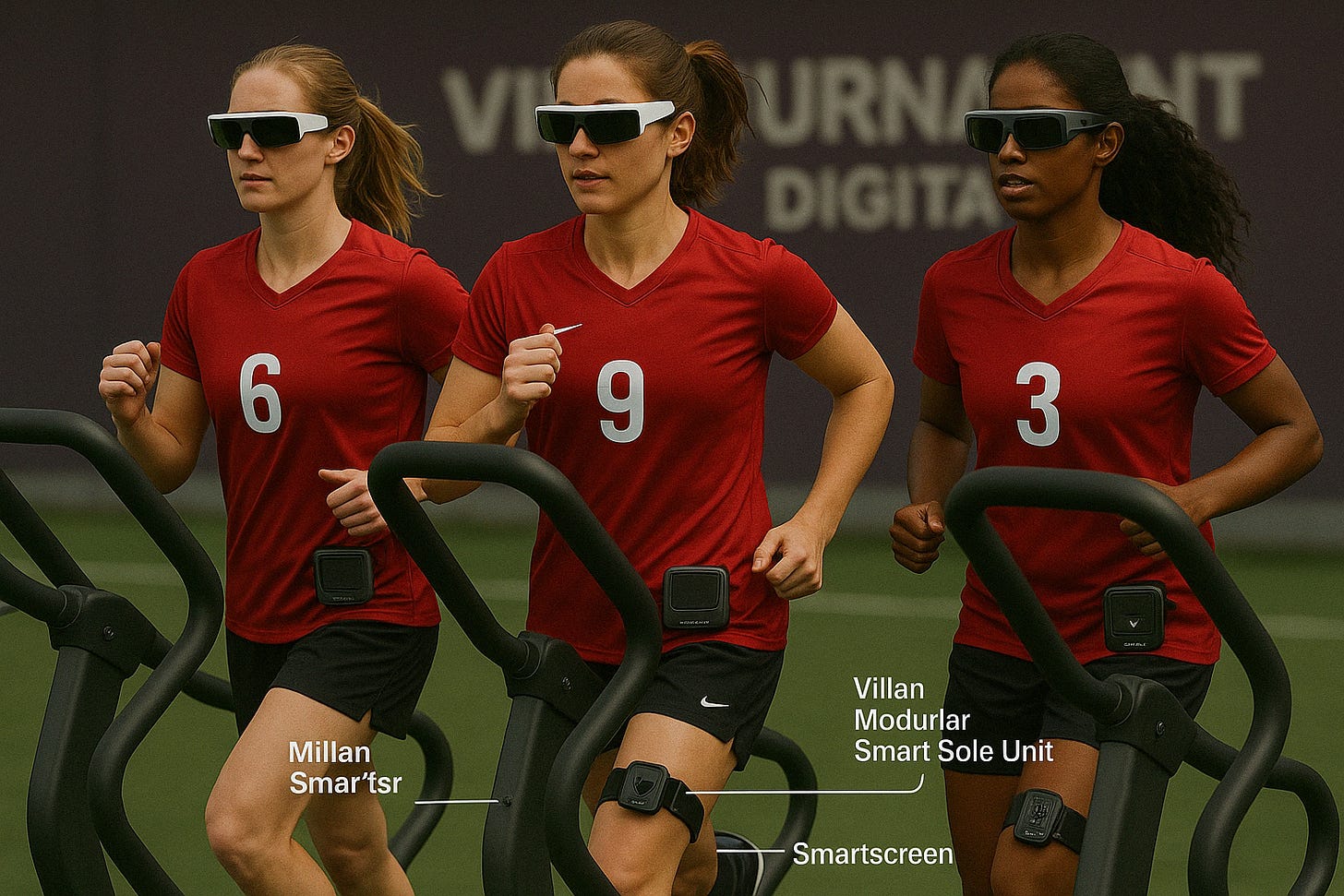
The Future of the Olympic Games: A Digital Augmented Reality Tournament with Wearable Tech
The Olympic Games are known for bringing together the world’s best athletes, but the future promises to take this tradition into the digital age, where the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and wearable technology will redefine how we experience and participate in global sporting events. Imagine a hybrid Olympic tournament, where athletes and spectators interact with the games in completely new ways, powered by smart glasses, smart shoes, smart hats, and other wearable devices, alongside digital environments that merge the real world with virtual elements.
1. The Integration of AR Glasses in the Olympic Experience
Augmented Reality (AR) glasses will play a central role
in enhancing the Olympic Games experience for both athletes and spectators:
For Athletes:
Real-Time Performance Data: Athletes will wear AR glasses equipped with heads-up displays (HUD), allowing them to see important performance metrics like speed, heart rate, caloric burn, biomechanics, and muscle fatigue in real-time. For example, a runner in the 100m sprint could see data on their stride length, optimal form, and time to goal, all while competing.Virtual Coaching: As athletes compete, virtual coaches can offer insights and adjustments in real-time through the AR glasses. Whether it's improving posture, adjusting grip, or recommending changes in running stride, the glasses will provide personalized advice based on live analysis of their movements.Performance Gamification: Athletes could participate in virtual competitions, with digital avatars of themselves competing against historical Olympic legends or even competing in real-time with other athletes worldwide. This gamified aspect could allow for virtual Olympic events that exist parallel to the physical tournaments.
For Spectators:
Enhanced Viewing: Spectators in the stands or at home will wear AR glasses that overlay real-time information about the athletes, events, and results. For instance, fans can access live statistics, replay options, and even get deeper insights into the athletes' training, preparation, and strategies.Interactive Viewing: AR glasses will allow fans to choose how they experience the events. They could, for example, switch between multiple camera angles, zoom in on key moments, or even select specific athletes to track during the competition. Fans might also participate in interactive polls or trivia while watching the games, enhancing engagement and making the experience more immersive.
2. Smart Shoes and Wearable Sensors for Athletes
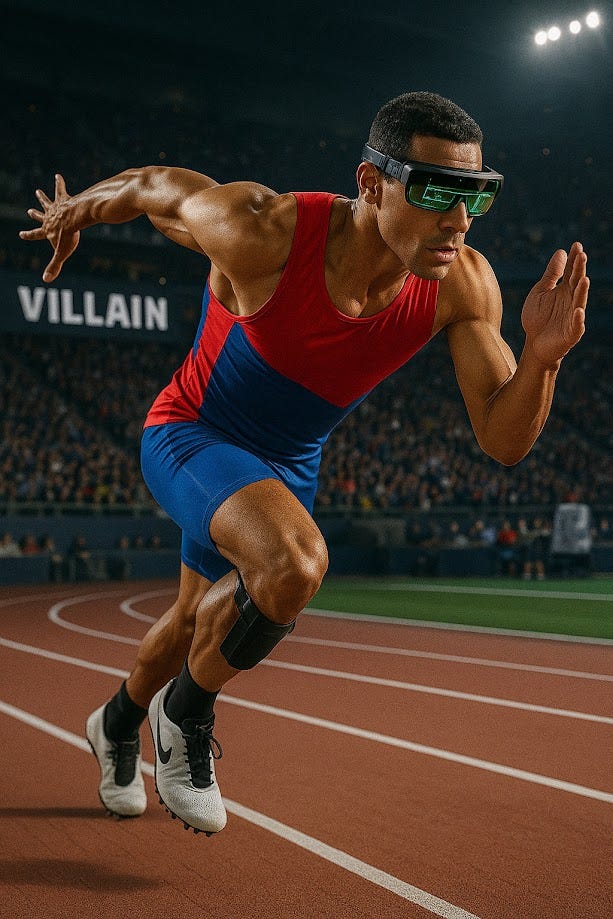
In this new Olympic paradigm, smart shoes and wearable sensors will be integrated into the competition, tracking performance and enhancing safety:
Smart Shoes for Track and Field Athletes: These shoes will come embedded with sensors that track gait, foot strike patterns, running speed, and step efficiency. In real-time, the shoes will provide feedback to help athletes adjust their techniques during training and live events. They can also be used to simulate the conditions of a virtual course to test an athlete’s endurance or skills before the real competition begins.Smart Shoes for Gymnastics or Diving: While they might not be directly used in every event, smart shoes could be used by athletes to track force and pressure distribution during gymnastic or diving routines, ensuring proper landings and minimizing the risk of injury. Sensors can assess whether athletes are executing moves correctly based on their biomechanics, providing feedback on how to improve their routines.
3. Smart Hats, Headgear, and AR Integration
Smart hats and headgear will offer additional safety and functionality, particularly for high-contact sports or activities where head protection is essential:
Head Impact Detection: In contact sports such as boxing, rugby, and football, smart helmets could include impact sensors that track the force and location of head impacts in real-time. This would provide an early warning system to coaches and medical teams if an athlete experiences a dangerous blow, helping to prevent concussions or head injuries.Cognitive Assistance for Mental Performance: Athletes in mentally demanding sports like equestrian events, archery, or shooting will benefit from smart hats that monitor brainwaves to detect signs of fatigue, stress, or focus levels. This data could then be used to suggest strategies for enhancing concentration and reducing anxiety.
4. Digital Simulation and Virtual Reality Training
AR and wearable technologies will also enable virtual Olympic simulators for athletes and fans to experience and interact with the games in ways never seen before.
Virtual Olympic Training: Before competing in the Olympic Games, athletes can train in virtual Olympic environments. Using VR and AR simulators, athletes will be able to practice on virtual tracks, swimming pools, and gymnastics facilities that mimic the exact conditions of the Olympic venues. These virtual environments can be customized for specific sports, allowing athletes to practice with real-time feedback, even if they are thousands of miles from the actual Olympic site.Simulated Fan Experiences: For fans, VR and AR will allow them to experience the Olympics in fully immersive, interactive digital environments. From the comfort of their homes, spectators can virtually attend the games, experiencing events from unique perspectives, such as from the point of view of the athletes, in the front row of the stadium, or from a drone-like aerial view of the Olympic village.
5. The Future of the Olympics: A Hybrid Digital Experience
The Olympic Games are undergoing a transformation that bridges the gap between the physical and digital worlds. With the integration of AR glasses, smart shoes, smart hats, and other wearable devices, athletes and fans will engage with the games in ways previously thought impossible. For athletes, these wearables will provide enhanced performance tracking, feedback, and training opportunities. For fans, the Olympics will become a more immersive, interactive, and globally accessible event.
In the coming years, as AR technology and wearable devices take center stage, the Olympics will no longer be limited to just the physical competition. The digital augmentation of the games promises a future where everyone, from athletes to fans, can experience the Olympics like never before—immersed in a world of real-time data, virtual simulations, and interactive entertainment that extends beyond the event itself.
6. Audience Experience: AR on Screens and TVs
While athletes are equipped with advanced wearables for enhanced performance and training, spectators at home or in the stadium will also enjoy a revolutionary viewing experience thanks to Augmented Reality (AR). By integrating AR into TV broadcasts and digital screens, viewers will be able to interact with the Olympics in ways that were once only imagined. Here’s how:
AR Integration for TV Viewers
AR Overlays on Screen: Television broadcasts of the Olympic events will feature AR overlays that enhance the real-time viewing experience. These overlays might include:Live Stats: Real-time data like athlete performance, speed, heart rate, and ranking will be displayed on the screen, dynamically updating as the competition progresses.3D Data Visualizations: AR can project 3D visualizations of athletes’ movements, trajectories, and techniques. For example, when a sprinter runs, viewers could see a digital 3D trail that shows their running form or compare their performance to that of previous Olympic champions.Instant Replay with AR Highlights: Spectators can experience instant replays enhanced with AR to highlight key movements, such as the arc of a javelin throw, or athlete posture in diving. These AR highlights could allow the viewer to focus on a specific aspect of the action from multiple angles with additional data.
Interactive Graphics: For complex sports like gymnastics, swimming, or cycling, AR graphics will allow viewers to zoom in on an athlete’s movements, see their techniques in slow motion, and even receive coach-like insights during the broadcast.
Interactive AR for Viewers at Home
AR Features for Home Viewers: When watching on smart TVs or through mobile apps, viewers can engage with interactive AR features. For example, viewers might be able to:
Choose from multiple camera angles, such as viewing the race from the perspective of different athletes or even from an aerial view using AR.Use AR to simulate the athlete’s motion on their own screen. If the sport involves complex movements (like a long jump or a pole vault), the viewer can watch the athlete in action, while the AR technology breaks down the physics behind the move in real-time.Use gesture controls to zoom in or out, or select specific stats that they want to follow, such as tracking a particular athlete’s heart rate, lap times, or velocity during a race.
Immersive Digital Environments for Fans
Enhanced Viewing: Fans watching the Olympics will be able to see the event through a digital filter that adds AR elements to the traditional broadcast. This could include:
Digital avatars of previous Olympic champions, highlighting their iconic moments in the sport or tracking their influence on the current event.
Virtual Sponsorships and Ad Placements: Brands could interact with viewers via virtual ads that are integrated into the viewing experience. These ads could pop up as 3D holograms on the athlete’s equipment, like a digital billboard on a sprinter’s shoe or floating around the arena.
Virtual Viewing Parties: Using VR and AR, viewers at home could host virtual Olympic parties where they attend in digital spaces, experiencing the game from within a virtual stadium while still being able to chat and cheer with friends in real-time, just like being there in person.
Fan Interaction with the Event
Real-Time Interaction: The Olympics would also offer interactive features where viewers can participate from their own homes. Whether it’s guessing who will win an event, making predictions on an athlete’s performance, or taking part in Olympic trivia in real-time, these interactions would be facilitated through AR overlays and apps.
Virtual Fan Engagement: Fans watching the games on their screens could use AR technology to interact with virtual mascots, athletes, or even perform virtual cheers. Fans could receive virtual "badges" for interacting with the event or attending digital spaces, much like gamification in sports video games.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap Between Physical and Virtual Reality
With AR overlays integrated into TV broadcasts and digital screens, the viewing experience of the Olympics will become far more interactive, engaging, and informative. Spectators will no longer just watch the event unfold—they will become an active part of the Olympic experience, whether it’s exploring data in real-time, engaging with virtual simulations of performances, or immersing themselves in digital environments. By blending the physical world of competition with the digital potential of AR, the Olympic Games will be more accessible, more exciting, and more personal than ever before.
As wearable tech and AR continue to evolve, future Olympic Games will not just be about watching athletes compete—they will be about participating in a shared digital experience that enhances the connection between athletes, fans, and the world. The digital future of the Olympics is here, and it’s only going to get more immersive and dynamic with each passing year.
Summary: The Future of Smart Wearables in Sports, Work, and Everyday Life
The next generation of smart wearables—from AR glasses and smart shoes to smart hats, belts, and even shoulders—represents a major leap forward in how we interact with technology. These devices integrate seamlessly into our daily lives, enhancing productivity, health, and entertainment by combining AI, AR, biometric sensors, and real-time data processing.
In the context of sports, wearables will play a vital role, enhancing both athletes’ performance and the viewing experience for fans. For athletes, devices like smart shoes can provide real-time feedback on gait and posture, improving movement efficiency and injury prevention. AR glasses will offer athletes real-time stats, immersive training simulations, and hands-free communication, allowing them to optimize their performance. Meanwhile, smart hats and shoulders will deliver support for safety, posture correction, and fatigue monitoring.
For spectators, AR-enhanced broadcasts will transform the Olympic Games into an interactive experience, displaying real-time data, 3D visualizations, and instant replays with AR overlays. Fans at home can enjoy the experience through smart TVs or mobile apps, engaging in virtual viewing parties and interacting with digital avatars of athletes, all while gaining deeper insights into the action through personalized stats and interactive features.
The future of wearables is also bright in other sectors. In work environments, wearables can monitor worker safety, ergonomics, and health, while in hospitals, they will support remote patient monitoring and health tracking. In education, wearables will enable immersive learning experiences and provide real-time data on students’ focus and well-being.
Ultimately, the core of this transformation lies in a unified computing system that connects all wearables, running on a central main OS. This system ensures cross-device synchronization, AI-powered insights, and real-time connectivity, creating a fully integrated and seamless user experience.
The future is clear: wearables will become an indispensable part of our lives, enhancing everything from sports and work to health, education, and entertainment. With a centralized platform managing and syncing all devices, the potential of smart wearables is vast, offering endless possibilities for improving human efficiency, safety, and interaction with the world.
Conclusion of Conclusions
Biometric smart wearables represent the convergence of cutting-edge technologies, transforming not just how we interact with the world, but how the world responds to us. Their integration into
smart homes,vehicles,healthcare,education, and everyday life paves the way for a future where personalized, real-time data drives smarter decisions, enhanced productivity, and improved well-being. These wearables are not just passive devices but active, interconnected elements of alarger intelligent ecosystemthat anticipates and responds to human needs in ways never before imagined.
As we move forward, the potential of biometric smart wearables to optimize human experience, enhance safety, and empower individuals cannot be overstated. The continued development of AI, biometrics, and connectivity will ensure that these devices evolve alongside our ever-changing needs. In this exciting new era of connectivity, we are witnessing the dawn of a truly augmented reality, where intelligent wearables seamlessly blend with our environment, making life smarter, safer, and more efficient.
Ultimately, the future of biometric wearables is boundless, offering limitless opportunities for improving health, transforming industries, and enhancing daily life. The integration of these devices into various sectors will set the stage for a connected world—one that is not just smart, but deeply intuitive and responsive to the dynamic nature of human existence.
The Conclusion of Conclusions
The evolution of smart wearables—driven by cutting-edge technologies like biometrics, AI, and IoT—marks the beginning of a new era where the boundaries between digital and physical realities blur. These wearables have become the cornerstone of an integrated, personalized world, where every aspect of human interaction with the environment is enhanced by intelligent, real-time data.
From smart homes and vehicles to healthcare, education, and gaming, the scope of impact is limitless. The power of biometric smart wearables is in their ability to adapt to the user’s unique needs, creating dynamic, responsive ecosystems that optimize efficiency, safety, and well-being across diverse sectors. They are not just tools, but extensions of human capability, offering profound implications for personal and professional life.
As we embrace a future where connected intelligence fuels the evolution of everyday life, the potential of these devices goes beyond simply enhancing experiences—they promise to redefine what it means to be human in a world where technology evolves hand in hand with us. The Conclusion of Conclusions is clear: we are entering a new age of seamless, intelligent interaction, where every wearable piece of technology is not just smart but deeply attuned to the individual, fostering a future that is safer, more efficient, and infinitely more connected.
This is the dawn of an era where the world doesn’t just respond to our actions—it anticipates them, and in doing so, creates a reality that is more intuitive, personalized, and dynamic than ever before. The potential is boundless, and the journey has just begun.
Final Conclusion
The evolution of smart wearables marks the dawn of a new era where technology seamlessly integrates with our daily lives, enhancing performance, health, safety, and entertainment. From AR glasses that bring immersive experiences to smart shoes that optimize movement and posture, these devices are transforming industries, sports, work environments, and everyday activities.
The power of AI, augmented reality, and biometric sensors combined with a unified computing system creates an interconnected ecosystem that allows wearables to communicate, adapt, and provide personalized insights in real-time. Whether it's enhancing an athlete’s performance, offering interactive sports simulations, enabling smart health monitoring, or transforming digital entertainment, the potential of these wearables is limitless.
As smart wearables continue to evolve, they will not only redefine personal experiences but will also revolutionize industries like sports, healthcare, education, work, and entertainment. With devices working in harmony, driven by centralized OS platforms and cross-device synchronization, wearables will usher in an era where human capability is enhanced, safety is prioritized, and digital experiences are deeply immersive and interconnected.
Thefuture of wearablesis one of boundless opportunity, where technology becomes an extension of our bodies, empowering us to achieve more and experience the world in new and exciting ways.
The Final Conclusion
The future of smart wearables is not just a technological leap—it's a transformative shift in how we experience the world, interact with our environments, and enhance our capabilities. From AR glasses providing immersive experiences to smart shoes optimizing performance and health, the integration of AI, augmented reality, and biometric sensors creates a connected ecosystem that is revolutionizing how we live, work, play, and engage with digital spaces.
These wearables are no longer standalone gadgets; they are part of an intelligent network that seamlessly interacts with each other and with the user. By combining real-time data processing, AI-driven insights, and personalized user experiences, these devices provide more than just functionality—they offer enhanced safety, performance, and convenience. Whether used in sports, healthcare, entertainment, or professional environments, wearables will continue to break boundaries and redefine our potential.
With technologies like augmented reality sports simulators, smart health monitoring, smart houses, and intelligent wearables integrated into various sectors, the role of wearables in society will only grow. As they evolve, the interconnected nature of these devices, powered by a centralized OS, will allow for new levels of customization, automation, and immersion.
In this new age, wearables will empower individuals and industries alike, unlocking new dimensions of efficiency, safety, and experience. As we move forward, the fusion of the physical and digital worlds will continue to blur, creating a future where human potential is amplified through technology. The era of smart wearables is just beginning, and its impact will resonate for generations to come.
Smart Shoes: Revolutionizing the Future of Footwear and Technology
Modular Smart Sole Unit: The Brain Beneath Your Feet | by Ronen Kolton Yehuda | Apr, 2025 | Medium
AR/VR Hybrid Smart Glasses: A Dual-Purpose Revolution | by Ronen Kolton Yehuda | May, 2025 | Medium
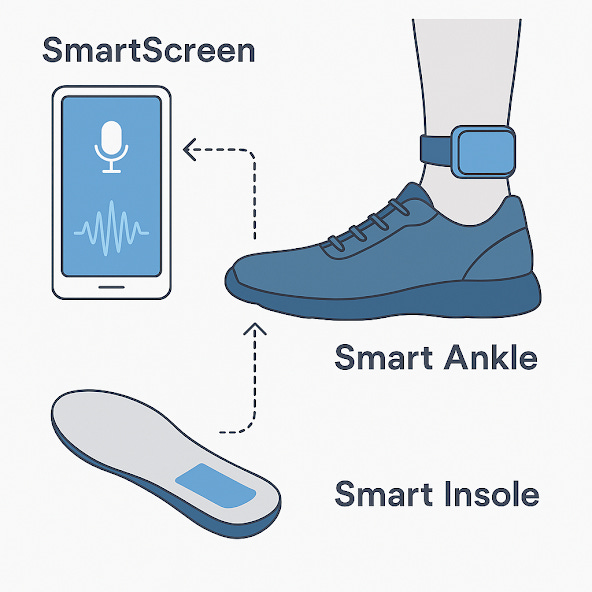
The Smart-Screen: The Future of Wearable Technology














































































Comments
Post a Comment